Mitozoa Search
The MitoZoa database can be queried using the "General Search" menu alone or in combination with one of the following specialized menus:1) Gene Order
2) Non-Coding Region (NCR)
3) Gene Content
Single entries are shown in the MZ format and can be also displayed/downloaded in EMBL-like and FASTA formats.
Entry lists can be downloaded in a tab-separated simple text format (.txt) or in a table format (.xls), and report different data depending on the search. The data included in these files consist at least of the following fields: Accession number, Definition, Taxonomy, Organism, Genome Length, and Molecule Topology.
The type and format of retrievable outputs for each search menu is reported below:
| Menu | Retrieved data | Format |
|---|---|---|
| General Search | Entry list Single entry |
tab-separated simple text (.txt) table (.xls) EMBL, FASTA |
| Gene Order | Entry list Gene order |
tab-separated simple text (.txt) table (.xls) FASTA-like |
| NCR | Entry list NCR sequences |
tab-separated simple text (.txt) table (.xls) FASTA |
| Gene Content | Entry list Gene sequences |
tab-separated simple text (.txt) table (.xls) FASTA |
General Search Menu
The "General Search Menu" allows text searches in all or in a single field of the MitoZoa entries, and is intended to provide information on general mtDNA features.In addition to standard fields of the EMBL format (such as AC number, Definition, Keywords, References, Organism Species, and Organism Classification), four MitoZoa-specific fields can be searched by this menu:
- Genetic Code
- Congeneric Species
- MitoZoa Reannotation Summary
- Base Composition.
Table 1. Translation tables describing the mitochondrial genetic codes used by Metazoa, according to the NCBI
| Name a | Number | Source |
|---|---|---|
| Vertebrate Mt Code | 2 | NCBI |
| Mold, Protozoan, and Coelenterate Mt Code and the Mycoplasma/Spiroplasma Code | 4 | NCBI |
| Invertebrate Mt Code | 5 | NCBI |
| Echinoderm and Flatworm Mt Code | 9 | NCBI |
| Ascidian Mt Code | 13 | NCBI |
| Table 5 with modified ATA meaning (Met->Ile) | 5mod | New b |
| Table 9 with modified AAA meaning (Asn->Lys) | 9mod | New c |
b: new translation table used by the two Porifera Hexactinellida, Iphiteon panicea (EF537576) and Sympagella nux (EF537577). This genetic code corresponds to translation table 5, except for the translation of ATA codon to Ile instead of Met. (Haen et al. 2007)
c: new translation table used by the Hemichordata Saccoglossus kowalevskii (AY336131). This genetic code corresponds to translation table 9, except for the translation of AAA codon to Lys instead of Asn (Smith, Beckenbach, and Scouras, unpublished).
- Congeneric Species
This check box allows the selection of all congeneric mtDNA entries belonging to a given taxon, which has to be defined by filling the "Taxonomy" text box. When the taxon is not defined (i.e. the "Taxonomy" box is left empty), the result consists of all congeneric species found in Metazoa.
- MitoZoa Reannotation Summary
All corrections and improvements of the original mtDNA entries, made through the MitoZoa semi-automatic reannotation pipeline, are summarized in the "MitoZoa Reannotation Summary" (MRS), which is shown in red in the MZ format and is included in the Comment field of the EMBL-like format.
The first standardized message of MRS indicates the entry AC number whose annotation was modified by MitoZoa: it can be a EMBL/Genbank/DDBJ or a RefSeq entry, being the latter marked by the presence of an underscore in the AC number. Other AC numbers derived from (i.e. RefSeq) or giving rise to (i.e. EMBL/Genbank/DDBJ) the above-mentioned reannotated mtDNA are possibly reported in the second standardized message (Figure 1).
The remaining portion of the "MitoZoa Reannotation Summary" (Figure 1) is divided into three sections, indicated by capitalized titles:
1) GENERAL REANNOTATION, which lists modifications concerning all EMBL fields, except the Feature Table (FT);
2) FEATURE TABLE REANNOTATION, which lists all modifications concerning the FT;
3) ADDITIONAL INFORMATION, which lists genomic information absent or not clearly reported in the original entry.
In each section, the type and source of entry corrections/improvements are described using standardized messages (Figure 1). Moreover, the "Modification Codes" (Mcode, Table 2) indicate the inference on which the modification was based or describe the type of modification. The Mcodes are always reported in square brackets. Table 3 reports the standardized messages used in the "MitoZoa Reannotation summary", and those associated to the corresponding modified FT lines.
Table 2. Modification codes (Mcodes) reported in the MitoZoa Reannotation Summary or associated to FTqualifier
| MCode | Meaning | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| IC | Inferred by Curator | Used for obvious erroneous annotations, i.e. tRNA genes with size > 105 bp; mtDNA topology; limits of "genes" different from that of "CDS" for protein-encoding genes without introns; etc |
| IR | Inferred by Reference | The reference is indicated only if different from that of the original entry, using the message "see PUBMED: number ". |
| IPA | Inferred by Program Analysis | Inferred by Blast, PatSearch, Arwen, or tRNAscanSE programs (Altschul et al. 1990; Lowe and Eddy 1997; Pesole, Liuni, and D'Souza 2000; Laslett and Canback 2008) |
| SE | Start codon Exception | Inferred by translation exception of the used genetic code. |
| NV | Not Validated | Feature not validated by the MitoZoa reannotation pipeline: it is followed by a more specific Mcode |
| AI | Annotation Improvement | Additional information improving the mtDNA annotation: it is followed by a more specific Mcode |
Figure 1. Structure of the "MitoZoa Reannotation Summary", including the list of used standardized messages.
The meaning of some standardized messages is explained within square brackets and gray background. The type of data is reported within < >. Alternative messages are separated by "or".
|
The genome annotation was derived from <INSDCa or RefSeq AC number>.
The sequence is also reported in <RefSeq or INSDC AC number>. [AC number derived from or giving rise to the reannotated mtDNA entry indicated in the previous line] GENERAL REANNOTATION modification of <field>: <standardized message>; [general structure of the standardized messages within this section] modification of the ID field: error in molecule topology [Mcode]; modification of the DE field: partial genome, missing part of the control region or missing control region or missing part of <gene:limits> [Mcode]; modification of the OS field: <free text> [Mcode] FEATURE TABLE REANNOTATION error in strand of <gene: corrected limits> [Mcode]; elimination of the erroneous < FTkey:limits> [Mcode]; [only for FTkey undoubtedly erroneous] unannotated <gene> at position <limits>; modified boundaries of <gene:new limits> (old: <old limits>); <gene_1> named as <gene_2>, and vice versa; [only for not-duplicated rRNA genes] <gene:limits > erroneously annotated in the original entry as <old gene name> [Mcode]; anticodon specificity modified from <old gene name> to <new gene name:limits> [Mcode]; [only for amino acids recognized by two tRNAs: anticodon specificity not reported or erroneous] trnM(CAU) <limits> specified as <initiator or elongator> [Mcode]; <gene:limits> not checked due to short size [Mcode]; [tRNA genes with size < 45 bp were not checked by the script-based MitoZoa tRNA reannotation pipeline due to inability of these genes to form a standard secondary structure] <gene:limits> not validated [Mcode]; [gene not validated by the MitoZoa reannotation pipeline] improvement of the <gene:limits> annotation by inclusion of start codon exception [Mcode]. ADDITIONAL INFORMATION <free text>; partial genome: missing part of the control region or missing control region or missing part of <gene:limits>; [partial genome, as defined by the presence of partial genes in the entry or by reference] presence of <group I or group II> intron in <gene:limits>; unidentified control region [Mcode]; [only for vertebrates: the control region was not-sequenced or not-annotated] unidentified <gene list> [Mcode]; [genes not-sequenced or unannotated] <gene> is not mitochondrially encoded; [only for usually mt-encoded genes, whose absence in the mtDNA was confirmed by reference check] <gene> is mitochondrially encoded; [only genes not usually mt-encoded] <5' or 3'> end of <rRNA gene:limits> not adjacent to the limit of flanking gene [Mcode]; both ends of <rRNA gene:limits> not adjacent to the limits of flanking genes [Mcode] |
a: INSDC indicates entries of the International Nucleotide Sequence Database Collaboration, comprising DDBJ, EMBL and GenBank primary databases.
Table 3. Standardized messages included in the "MitoZoa Reannotation Summary" and in FT lines, together with the possible gene categories involved in each message type. Messages are listed according to the Section of the "MitoZoa Reannotation Summary" containing them.
Alternative messages are separated by "or". The type of data is reported within < >. CDS: protein-coding genes
| "MitoZoa Reannotation Summary" message | FTqualifier "/note" | FTqualifier "/inference" a | Gene | Mcode b |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| none | putative NCR limits due to uncertain rRNA boundaries | NCR | IC | |
| none | putative NCR c | NCR | IC | |
| none | NCR inside intron | NCR | IC | |
| none | Longest NCR | NCR | IC | |
| none | unusual anticodon: <AC> | profile:Arwen:1.2 | tRNA | AI:IPA |
| none | short tRNA validated by reference | tRNA | IR | |
| In "Feature Table Reannotation" section | ||||
| Message | FTqualifier "/note" | FTqualifier "/inference" | Gene | Mcode |
| error in strand of <gene:corrected limits> | error in strand annotation | nucleotide motif:PatSearch:2.0; profile:<tRNAscanSE:1.23 or Arwen:1.2> |
tRNA | IPA, IR |
| error in strand of <gene:corrected limits> | error in strand annotation | alignment:blastn | rRNA | IPA, IR |
| elimination of the erroneous <gene:limits> | All | IC, IR | ||
| unannotated <gene> at position <limits> | added by MitoZoa Curator | All | IC, IR | |
| modified boundaries of <gene:new limits> (old: <old limits>) | modified gene boundaries <and anticodon specificity> | profile:<tRNAscanSE:1.23 or Arwen:1.2> | tRNA | IPA |
| <gene_1> erroneously annotated in the original entry as <gene_2>, and vice versa | error in gene name | alignment:blastn | rRNA | IPA, IC, IR |
| <gene:limits> erroneously annotated in the original entry as <old gene name> | error in gene name | alignment:blastn | rRNA | IPA, IC, IR |
| <gene:limits> erroneously annotated in the original entry as <old gene name> | error in gene name | profile:Arwen:1.2 or nucleotide motif:PatSearch:2.0 | tRNA | IPA, IC, IR |
| anticodon specificity modified from <old gene name> to <new gene name:limits> | modified anticodon specificity | nucleotide motif:PatSearch:2.0; profile:tRNAscanSE:1.23 or Arwen:1.2 |
tRNA | IPA |
| none | putative NCR limits due to uncertain rRNA boundaries | NCR | IC | |
| none | putative NCR c | NCR | IC | |
| trnM(CAU):<limits> specified as <initiator or elongator]> | specified as <initiator or elongator]> trnM(CAU), based on signals present in primary and secondary structures | profile:<tRNAscanSE:1.23 or Arwen:1.2]> | tRNA | IPA |
| <gene:limits> not checked due to <short or long>size | not checked due to [short or long] size | tRNA | NV:IC | |
| <gene:limits> not validated | <not validated by PatSearch and Arwen check>or<not validated due to positions with ambiguous bases in anticodon arm> | tRNA | NV:IPA | |
| improvement of the <gene:limits> annotation by inclusion of start codon exception | <sequence> seems to be translated as start codon | CDS | AI:SE | |
| In "Additional Information" section | ||||
| Message | FTqualifier "/note" | FTqualifier "/inference" | Gene | Mcode |
| 5'end of <rrn:limits> not adjacent to the limit of flanking gene | 5'end not adjacent to the limit of flanking gene | rRNA | AI:IC | |
| 3'end of <rrn:limits> not adjacent to the limit of flanking gene | 3'end not adjacent to the limit of flanking gene | rRNA | AI:IC | |
| both <rrn:limits> ends not adjacent to the limits of flanking genes | both ends not adjacent to the limits of flanking genes | rRNA | AI:IC | |
| <gene_1:limits> contains the entire <gene_2:limits>, which is encoded on the <complementary or same> strand | contains the entire <gene_2:limits>, which is encoded on the <complementary or same>strand | All | AI:IC, AI:IR | |
| " | <entirely> contained in <gene_1:limits>, which is encoded on the <complementary or same> strand | All | AI:IC, AI:IR | |
b: as reported in Table 2.
c: only for NCRs 1 bp long
- Base Composition
This sub-menu allows the selection of all mtDNA entries having a specific base composition.
Entries can be selected based on the min, max, and range of the following parameters, calculated on the whole mtDNA sequence and on the strand stored in the database:
- percentage of single bases (where "N" indicates any base different from A,C,G, T),
- GC percentage,
- AT_skew and GC_skew.
The GC_skew and AT_skews indicate compositional differences between the two DNA strands, and were calculated according to the formulae by Perna and Kocher (1995):
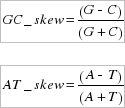
where C, G, A, and T are the occurrences of the four bases on the whole mtDNA sequence and on the strand stored in the database. Skew values range from -1 to +1, with a value equal to zero corresponding to the absence of compositional strand asymmetry.
Gene Order Menu
The gene order is reported as a string of standardized gene names (Table 4), with a "-" sign preceding genes encoded by the minus strand. Genes interrupted by introns or splitted in two parts are indicated with the standardized gene name followed by "_5" or "_3" for the 5'- and 3'-end, respectively.For complete circular mtDNAs, the first gene of the string is always nad1; for partial and linear mtDNAs, the first gene of the string is the first gene annotated in the Feature Table of the entry.
The gene order is reported in a FASTA-like format (Figure 2) that can be downloaded and directly used as input in programs analysing gene order such as CREx (Bernt et al. 2007).
- "Search for Gene Order"
This sub-menu enables the retrieval of all mtDNA entries having a given string of two or more genes. Each gene string is searched in both the forward and reverse/complement orientation (i.e. the string "nad4L nad4 -nad6" is searched also as "nad6 -nad4 -nad4L"), as these orientations are biologically equal and depend only on the strand stored in the database.
The gene string can be directly written into the relevant box using the standardized gene names (Table 4), or it can be generated via the "Add gene name" button. This tool allows user to consecutively select the genes of interest from a drop-down list, and to automatically write them in the relevant text box.
- "Gene order as in"
This sub-menu allows retrieving:
1) all mtDNA entries whose gene order is equal to that of a given species, selected using a drop-down list;
2) all gene orders present in a given taxonomic group, whose name has to be written in the "Genus or higher taxonomic rank" text box.
- "Output dataset type"
This sub-menu allows selecting the gene order output among one of the following datasets, containing:
1- All genes
2- No tRNA (i.e. all genes excluding tRNAs)
3- Only CDS (i.e. only protein genes)
The check box "Show notes on non-validated genes" permits to display/download gene order dataset(s) containing the flag "[NV]" (Not Validated) after each gene that was not-validated by the MitoZoa pipeline, and thus has uncertain annotation. This option helps user to identify the most controversial points of mtDNA annotations and gene order.
Figure 2. Example of FASTA-like format reporting the gene order of three MitoZoa entries
| >NC_001807|Homo sapiens nad1 trnI -trnQ trnM nad2 trnW -trnA -trnN -trnC -trnY cox1 -trnS(UCN) trnD cox2 trnK atp8 atp6 cox3 trnG nad3 trnR nad4L nad4 trnH trnS(AGY) trnL(CUN) nad5 -nad6 -trnE cob trnT -trnP trnF rrnS trnV rrnL trnL(UUR) >NC_001808|Ceratotherium simum nad1 trnI -trnQ trnM nad2 trnW -trnA -trnN -trnC -trnY cox1 -trnS(UCN) trnD cox2 trnK atp8 atp6 cox3 trnG nad3 trnR nad4L nad4 trnH trnS(AGY) trnL(CUN) nad5 -nad6 -trnE cob trnT -trnP trnF rrnS trnV rrnL trnL(UUR) >NC_001816|Cepaea nemoralis nad1 nad4L cob trnD trnC trnF cox2 trnY trnW trnG trnH -trnQ -trnL(UUR) -atp8 -trnN -atp6 -trnR -trnE -rrnS -trnM -nad3 -trnS(UCN) -trnT -cox3 trnS(AGN) nad4 trnI nad2 trnK cox1 trnV rrnL trnL(CUN) trnA nad6 trnP nad5 |
Table 4. Standardized names and NCR codes for the mt genes of Metazoa
| Product 1 | Gene Code | NCR code 2 |
|---|---|---|
| ATP synthase subunit 6 | atp6 | A6 |
| ATP synthase subunit 8 | atp8 | A8 |
| ATP synthase subunit 9 | atp9 | A9 |
| cytochrome b | cob | CB |
| cytochrome c oxidase subunit I | cox1 | C1 |
| cytochrome c oxidase subunit II | cox2 | C2 |
| cytochrome c oxidase subunit III | cox3 | C3 |
| NADH dehydrogenase subunit 1 | nad1 | N1 |
| NADH dehydrogenase subunit 2 | nad2 | N2 |
| NADH dehydrogenase subunit 3 | nad3 | N3 |
| NADH dehydrogenase subunit 4 | nad4 | N4 |
| NADH dehydrogenase subunit 4L | nad4L | 4L |
| NADH dehydrogenase subunit 5 | nad5 | N5 |
| NADH dehydrogenase subunit 6 | nad6 | N6 |
| Unusual protein-coding genes | ||
| Unknown or hypothetical protein 3 | orf | OR |
| Putative DNA/RNA polymerase | dnaB | DB |
| Homing endonuclease | heg | HG |
| DNA mismatch repair protein mutS | mutS | US |
| SecY-independent transporter protein 4 | mttB | MB |
| Ribosomal RNA genes | Large ribosomal subunit RNA | rrnL | RL |
| Small ribosomal subunit RNA | rrnS | RS |
| Transfer RNA genes | ||
| tRNA-Ala | trnA | TA |
| tRNA-Cys | trnC | TC |
| tRNA-Asp | trnD | TD |
| tRNA-Glu | trnE | TE |
| tRNA-Phe | trnF | TF |
| tRNA-Gly | trnG | TG |
| tRNA-Gly(AGR) | trnG(AGR) | GA |
| tRNA-Gly(GGN) | trnG(GGN) | GG |
| tRNA-His | trnH | TH |
| tRNA-Ile | trnI | TI |
| tRNA-Ile(CAU) | trnI(CAU) | IC |
| tRNA-Lys | trnK | TK |
| tRNA-Leu(CUN) | trnL(CUN) | LC |
| tRNA-Leu(UUR) | trnL(UUR) | LU |
| tRNA-Met | trnM | MC |
| tRNA-Met(UAU) | trnM(UAU) | MU |
| Elongator tRNA-Met | trnM(CAU)e | ME |
| tRNA-FormylMet | trnM(CAU)f | MF |
| tRNA-Asn | trnN | TN |
| tRNA-Pro | trnP | TP |
| tRNA-Gln | trnQ | TQ |
| tRNA-Arg | trnR | TR |
| tRNA-Arg(UCU) | trnR(UCU) | RU |
| tRNA-Ser(AGY) | trnS(AGY) | SA |
| tRNA-Ser(AGN) | trnS(AGN) | SA |
| tRNA-Ser(UCN) | trnS(UCN) | SU |
| tRNA-Thr | trnT | TT |
| tRNA-Unknown 5 | trnUk | UK |
| tRNA-Val | trnV | TV |
| tRNA-Trp | trnW | TW |
| tRNA-Tyr | trnY | TY |
1: The different tRNA genes for Gly, Ser and Leu are named based on the recognized codons, while the different tRNA genes for Met, Arg e Ile are named based on the anticodon sequence.
2: Abbreviations used for the definition of the Non-Coding Regions (NCR) code (see NCR section).
3: Used to indicate several non-homologous ORFs.
4: Synonymous gene names: tatC, ymf16.
5: tRNA or tRNA-like genes with an unexpected anticodon.
NCR Menu
The NCR menu allows the retrieval and download of non-coding regions (NCR) having:1) a given bp length (min, max, or range);
2) a given gene upstream and/or downstream the NCR itself. If the NCR is at the beginning or at the end of a linear or partial mtDNA, then the "5'end" and "3'end" codes are used to retrieve these NCRs. The standardized gene names are reported in Table 4.
A NCR is defined as a non-coding sequence of any size located between two consecutive annotated genes: "misc_feature", "D-loop" and all other non-genic FTkeys have not been considered in the NCR boundary definition, thus, if present, they have been included in NCR sequences. Finally, all NCRs are in the plus orientation (i.e., the same orientation of the entry sequence).
Each NCR has been associated to a specific code summarizing data on species, flanking genes, and bp length of the NCR itself. This code is reported in the MitoZoa-specific FTqualifier "code", and is made up of 3 compulsory and 2 optional bits, spaced out by underscores:
1) Species bit (compulsory): 4 letters for species name. Table 5 lists the species bits for all entries;
2) Gene bit (compulsory): 2 letters for the gene preceding NCR + 2 letters for the gene following NCR (see NCR codes in Table 4). If the NCR is at the beginning or at the end of a linear or partial mtDNA, the first/last part of this bit will be "5E" (meaning: 5'-end) and "3E" (meaning: 3'-end), respectively;
3) Length bit (compulsory): the length of NCR in bp;
4) Intron bit (optional): the "ii" bit, an acronym for "inside intron", indicates NCR sequences located inside a group I or group II intron;
5) Gene copy number bit (optional): 2 letters for the copy-number of the gene upstream NCR + 2 letters for the copy-number of the gene downstream NCR. Thus, if the gene upstream (downstream) NCR is present in the mtDNA in multiple copies, then a " uj "(" dj ") bit is used, being "j" the gene copy number defined by the position in which this multi-copy gene appears in the FT, and "u" ("d") an abbreviation for "upstream" ("downstream").
As an example, a NCR of Halocynthia roretzi, located between nad6 and the second copy of trnF, having a length of 36 bp, will be named in the "code" FTqualifier as: AAGZ_N6TF_36_d2.
As further comments, the longest NCR of a mtDNA entry is indicated with the standardized message "note= longest non-coding region", and NCR contained in group I or group II introns are indicated with the standardized message "note= NCR inside intron".
Table 5: Species bits, organism and accession number (AC) for all entries in MitoZoa DB
Click here to show Table 5
Click here to Download Table 5 (xls format)
Gene Content Menu
This menu allows to obtain statistics on the mtDNA gene content, and to retrieve sub-sequences corresponding to specific genes or FTkeys.- "Gene count"
This sub-menu allows retrieving:
1) all mtDNA entries encoding for a specific number of genes, referred to the whole gene content or to a given gene category (tRNA, rRNA or CDS: protein coding genes) that can be selected using a drop-down list. This search can be also limited to only one strand;
2) all mtDNA entries where a given gene is absent, i.e. the gene is not encoded by the mtDNA, or is not present in the mtDNA entry either because of partial genome or unannotated gene. The standardized gene names are reported in Table 4 and can be combined using the "AND" Boolean operator.
3) all mtDNA entries where a gene is present in at least two copies (duplicated). The standardized gene names are reported in Table 4 and can be combined using the "AND" Boolean operator.
- "Feature retrieval"
This sub-menu allows retrieving:
1) all sequences of a specific gene, whose standardized name can be selected using a drop-down list;
2) all sub-sequences belonging to a specific FTkey category, which can be selected using a drop-down list; Additionally, both searches can be restricted setting a limit for the length (in bp) and the strand of the selected gene/FTkey. If the length text boxes are not filled, genes/FTkeys of any length are shown.
References
Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. 1990. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol 215:403-410.
Bernt M, Merkle D, Ramsch K, Fritzsch G, Perseke M, Bernhard D, Schlegel M, Stadler PF, Middendorf M. 2007. CREx: inferring genomic rearrangements based on common intervals. Bioinformatics. 23:2957-2958.
Haen KM, Lang BF, Pomponi SA, Lavrov DV. 2007. Glass sponges and bilaterian animals share derived mitochondrial genomic features: a common ancestry or parallel evolution? Mol Biol Evol. 24:1518-1527.
Laslett D, Canback B. 2008. ARWEN: a program to detect tRNA genes in metazoan mitochondrial nucleotide sequences. Bioinformatics. 24:172-175.
Lowe TM, Eddy SR. 1997. tRNAscan-SE: a program for improved detection of transfer RNA genes in genomic sequence. Nucleic Acids Res. 25:955-964.
Perna NT, Kocher TD. 1995. Patterns of nucleotide composition at fourfold degenerate sites of animal mitochondrial genomes. J. Mol. Evol. 41:353-358.
Pesole G, Liuni S, D'Souza M. 2000. PatSearch: a pattern matcher software that finds functional elements in nucleotide and protein sequences and assesses their statistical significance. Bioinformatics 16:439-450.



